NoSQL Databases



NoSQL databases, also known as "Not Only SQL," are non-relational databases that do not adhere to the traditional table-based structure of relational databases. Unlike relational databases, which use a fixed schema, NoSQL databases use a flexible schema that allows for the storage and retrieval of unstructured and semi-structured data.
NoSQL databases are best suited for handling large amounts of data that cannot be easily modeled in a relational schema. They are often used in big data and real-time web applications, where the ability to scale horizontally and handle high write loads is a must. Some popular NoSQL databases include MongoDB, Cassandra, and Redis.
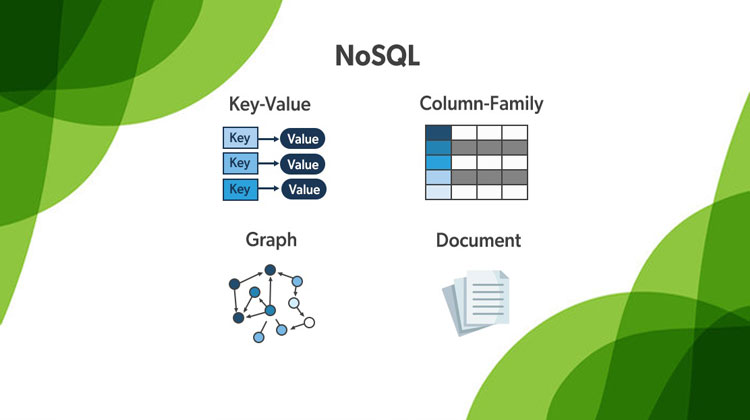
This stores information in JSON documents instead of columns and rows used by relational databases. To be clear, NoSQL stands for “not only SQL” rather than “no SQL” at all. This means a NoSQL JSON database can store and retrieve data using literally “no SQL.” Or you can combine the flexibility of JSON with the power of SQL for the best of both worlds. Consequently, NoSQL databases are built to be flexible, scalable, and capable of rapidly responding to the data management demands of modern businesses. The following defines the four most-popular types of NoSQL database:
Another advantage of NoSQL databases is their ability to handle unstructured and semi-structured data. Relational databases require data to be stored in a specific, predefined structure, which can be limiting when working with data that does not fit neatly into a table. NoSQL databases, on the other hand, can store data in a variety of formats, including JSON and XML, making them more flexible and better suited for handling data that is not easily structured.
NoSQL databases also have their own set of challenges. One of the biggest challenges is the lack of support for complex queries, which can make it difficult to retrieve and analyze specific subsets of data. Additionally, NoSQL databases do not typically support transactions, which can make them less suitable for certain types of applications.
In conclusion, NoSQL databases are a powerful tool for handling large amounts of unstructured and semi-structured data. They are highly scalable and can be easily distributed across multiple servers, making them well-suited for big data and real-time web applications. However, they do have their own set of challenges, particularly when it comes to complex queries and transactions, so it's important to carefully consider the use case before deciding to implement a NoSQL database.
Multi-modal databases leverage some combination of the four types described above and therefore can support a wider range of applications.
NoSQL databases use a horizontal scale-out methodology that makes it easy to add or reduce capacity quickly and non-disruptively with commodity hardware. This eliminates the tremendous cost and complexity of manual sharding that is necessary when attempting to scale RDBMS
By simply adding commodity resources, enterprises can increase performance with NoSQL databases. This enables organizations to continue to deliver reliably fast user experiences with a predictable return on investment for adding resources—again, without the overhead associated with manual sharding.
NoSQL databases are generally designed to ensure high availability and avoid the complexity that comes with a typical RDBMS architecture that relies on primary and secondary nodes. Some “distributed” NoSQL databases use a masterless architecture that automatically distributes data equally among multiple resources so that the application remains available for both read and write operations even when one node fails.
By automatically replicating data across multiple servers, data centers, or cloud resources, distributed NoSQL databases can minimize latency and ensure a consistent application experience wherever users are located. An added benefit is a significantly reduced database management burden from manual RDBMS configuration, freeing operations teams to focus on other business priorities.
NoSQL offers the ability to implement flexible and fluid data models. Application developers can leverage the data types and query options that are the most natural fit to the specific application use case rather than those that fit the database schema. The result is a simpler interaction between the application and the database and faster, more agile development.
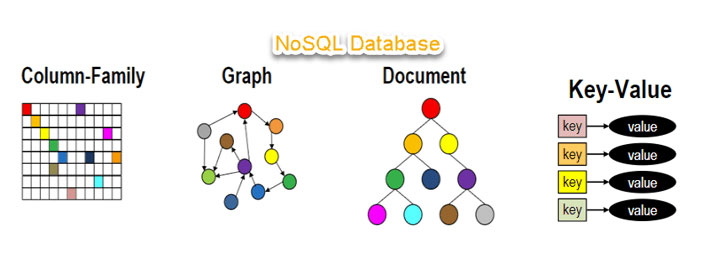
This emphasize simplicity and are very useful in accelerating an application to support high-speed read and write processing of non-transactional data. Stored values can be any type of binary object (text, video, JSON document, etc.) and are accessed via a key. The application has complete control over what is stored in the value, making this the most flexible NoSQL model. Data is partitioned and replicated across a cluster to get scalability and availability. For this reason, key value stores often do not support transactions. However, they are highly effective at scaling applications that deal with high-velocity, non-transactional data.
Document databases typically store self-describing JSON, XML, and BSON documents. They are similar to key-value stores, but in this case, a value is a single document that stores all data related to a specific key. Popular fields in the document can be indexed to provide fast retrieval without knowing the key. Each document can have the same or a different structure.
Wide-column NoSQL databases store data in tables with rows and columns similar to RDBMS, but names and formats of columns can vary from row to row across the table. Wide-column databases group columns of related data together. A query can retrieve related data in a single operation because only the columns associated with the query are retrieved. In an RDBMS, the data would be in different rows stored in different places on disk, requiring multiple disk operations for retrieval.
A graph database uses graph structures to store, map, and query relationships. They provide index-free adjacency, so that adjacent elements are linked together without using an index.
Hope we can share a breaf idea on this topic. If you have any suggestions or questions, please reach us by leave your comment below. thank you...
Leave Your Comment Here